Corn, also referred to as maize, is one of the most extensively grown crops in the world. It is used as a basic nutrition ingredient and animal fodder as well as being a critical component in numerous industrial processes. Corn production is important for global trade, agricultural economies, and for food security worldwide.
Corn producers contribute to global development efforts by ensuring a constant and ample supply for the crop’s domestic use and export.
Indeed, a slightly higher corn production in some of the biggest corn-producing nations can help to reduce hunger and malnutrition and enhance the general well-being of people worldwide, particularly in countries and areas that are highly dependent on corn such as Nigeria, Malawi, and Guatemala.
Global corn production
Although initially predicted to hit 1.17 billion metric tons in 2023, slightly less corn was actually produced globally – 1.15 billion. However, the International Grains Council (IGC) has predicted that global corn production will rise significantly to a historic 1.233 billion metric tons in the 2024–2025 marketing year. Market growth is anticipated to be fueled by factors such as the growing population, a rising demand for animal fodder and industrial use, and increasing corn starch use.
Today, due to rising corn output and improved technology advances which help to increase corn yields, Northern and Southern America, and Asia Pacific are two well-established producers accounting for a sizable proportion of the worldwide corn market.
In the 2023-2024 marketing year, the United States produced 389.7 million metric tons of corn, about one-third of the world’s total, making it the largest corn producing country. Completing the top three corn-producing nations are China and Brazil.
Corn production in developing countries
The economies of numerous developing nations are highly dependent on agriculture and by growing corn, these countries could lessen their reliance on imports and increase the availability of cheap, wholesome food for their people.
Most of the food produced in developing nations is on a small scale and is made up primarily of staple crops such as corn, wheat, and rice. Millions of African, South Asian, and Latin American citizens depend heavily on corn.
As an essential agricultural activity, corn production is important to the economies and economic growth of these countries. Small-scale farmers also benefit financially from it and its production impacts upon job creation and helps to ensure food security for the local population.
Risks faced by developing countries in corn production
Although all sorts of agricultural threats directly lead to low production and food insecurity for rural communities in developing nations, weather-related disasters are among the most prevalent hazards.
Hazards such as drought and floods, which obliterate crops in the field and slow the growth of fodder that animals require to survive, are a concern for those working in the agricultural sector in developing countries. In addition, market hazards such as fluctuating prices for agricultural production also pose risks.
Furthermore, corn is a crop that is susceptible to fungal infections that result in the production of toxic byproducts. Although common in corn, these mycotoxins differ depending on the region and can have negative effects on human and animal health. Managing corn’s mycotoxins (such as through the cultivation of corn varieties that are resilient to aflatoxins and fumonisins) is rather difficult, particularly in developing countries where corn is used as a staple food.
Top corn producers in the world
Major corn-producing nations play an important role in global trade with their corn exports enabling countries to satisfy domestic demand and take part in regional and international trade networks. Supporting transparent and equitable trade norms, and facilitating access to market developing countries are some of the main goals of international development initiatives.
Corn production world map
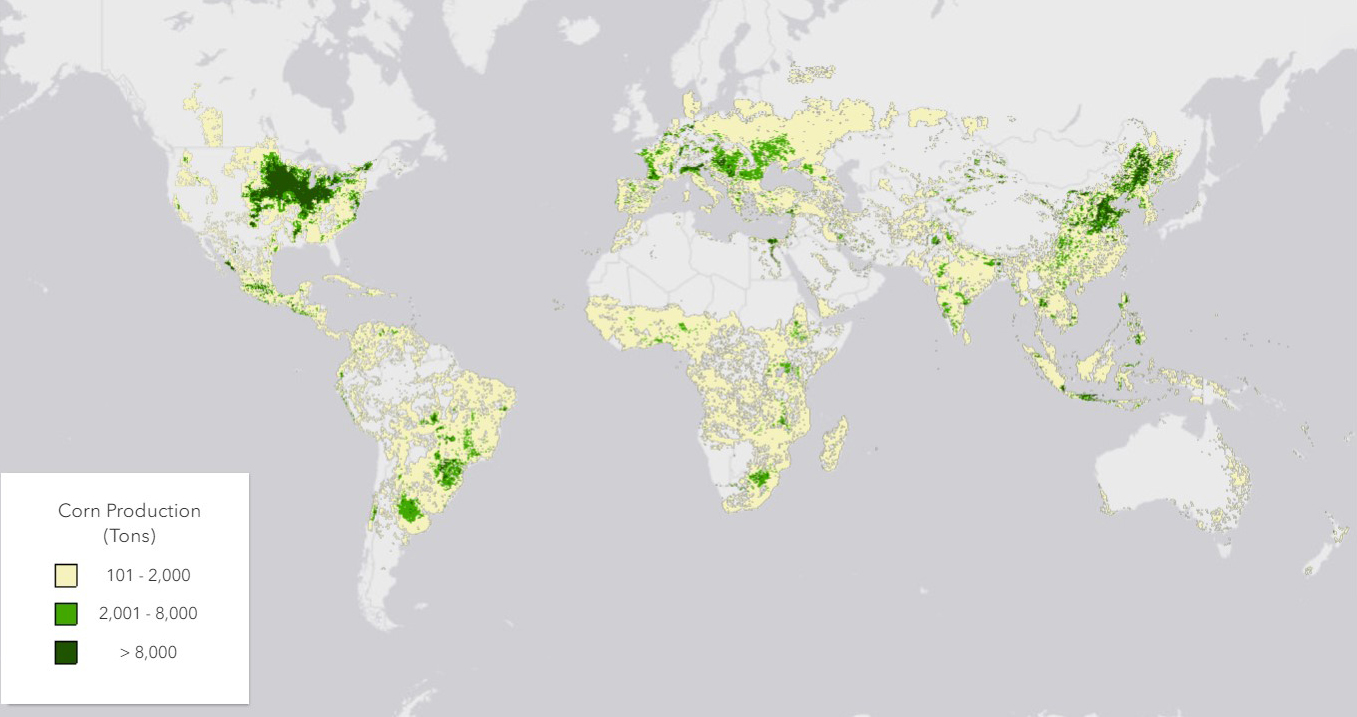
Source: USDA
The US Department of Agriculture‘s March 2024 report lists these countries as the major corn producers worldwide:
 The United States of America
The United States of America
Corn is the most important fodder crop in the United States, accounting for over 95% of the country’s fodder output and use. The US is the world’s biggest producer of corn accounting for 32% of global corn production – or almost 390 million metric tons. Every year, farmers in the United States plant approximately 90 million acres of corn.
 China
China
Based on the March report from WASDE, China’s estimated corn production for 2023–2024 grew by 4.2% to reach 288.8 million tons, despite early concerns that crops in the regions with high productivity had been harmed by typhoons and heat. A record corn yield was achieved as a result of a larger area being planted and higher precipitations, and also due in part to improvements in agricultural policy.
 Brazil
Brazil
Brazil has increased its corn acreage by 72% during the past 20 years from 31.6 million acres in 2003 to nearly 55 million acres in 2022. The latest data shows that Brazil produced 124 million metric tons of corn, which constitutes around 10% of the total global production of the crop. The American Foreign Agricultural Service (FAS) predicts that Brazil’s corn output will reach 129 million metric tons in the 2024–25 crop year.
 European Union
European Union
Because feeding livestock requires additional nutrition in the form of protein, the EU’s need for corn is being driven by the rapidly expanding livestock sector and the commercial compound feed business. Additionally, as people’s awareness of their health has grown, they have developed a taste for diets high in protein which has increased demand for grains like corn.
Romania, France and Poland are the EU’s biggest corn producers. Today, the region produces over 60 million metric tons of corn with 63.7 million tons expected to be harvested in 2024.
 Argentina
Argentina
The corn industry plays a crucial role in this country and today Argentina ranks third in terms of corn exports, following Brazil and the U.S. However, Argentina’s corn crop has had an emotional ride in the past few years. Despite the fact that the country is experiencing its worst drought in over 60 years, which has repeatedly caused drastic harvest reduction, it still managed to remain in the top 5 major corn producers.
During the 2021/2022 season, corn production decreased by 3 million tons, dropping to 49.5 million. The following season, the fall was even more painful with corn production being 36 million tons. However, the 2023/2024 season registered a huge recovery and, as a result of favorable weather conditions, the production figure hit 56 million tons.
Top 10 corn producers worldwide (in 1000 metric tons)
Source: USDA
Final word
The top-10 biggest corn-producing nations play a crucial role in supplying the world with this important crop. With their large corn production capacities, these countries not only help to ensure global food security but also have a huge influence on agriculture and worldwide trade.
At the same time, corn production faces serious issues such as natural hazards, pests, and diseases which all have a serious impact on the sector in both developing and developed countries. While developing countries face issues tackling these issues, developed countries can utilize developments in agricultural practices, technology, and research to stabilize and even increase the productivity and efficiency of corn farming.
Finally, it is worth noting that in order to preserve the long-term survival and resilience of the corn sector, the major corn-producing nations need to concentrate on sustainable farming practices, resource management, and innovation.
See also: Top 10 cocoa-producers and the issue of child labor in the industry

