The United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA) is one of the key United Nations agencies which focuses on improving maternal and reproductive health around the globe.
The UNFPA began operations in 1969 when it was known as the United Nations Fund for Population Activities (hence the acronym UNFPA). The agency was then part of the United Nations Development Fund (now the UNDP), with a specific mission to direct resources specifically to improving maternal and reproductive health and curbing unwanted population growth, while its parent organization (the UNDP) aimed at improving the quality of life of all people, and promote sustainable human and economic development.
Thus, initially, the organization was subordinated to the United Nations Development Fund (now the United Nations Development Program or UNDP) but was reallocated to being directly under the aegis of the UN General Assembly in 1971.
Since its inception, the UNFPA focused primarily on collecting statistics about maternal and child health as well as performing analysis of existing sociological trends. However, following the 1994 International Conference on Population and Development (ICPD), the UNFPA moved toward taking a more proactive role in providing education, funding, and resources to help change individual member countries’ family planning and reproductive health policies.
In 1987, the UNFPA was renamed the United Nations Population Fund. However, the UNFPA acronym is still used.
In 2018, the UNFPA resolved that it would focus on achieving three goals: the end of unmet need for family planning, the end of preventable maternal deaths, and the end of gender-based violence. These goals are designed to be compatible with both the UN 2030 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) as well as the 1994 ICPD Program of Action which seeks to combat population growth.
The UNFPA is headquartered in New York City and has 129 field offices around the globe. The agency employs approximately 1,200 people.
What Is the UNFPA?
The United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA) is the world’s largest organization that provides funding and resources for reproductive health and population control. The organization’s integrated budget for 2022-2025 estimates $5,497.4 million. According to the UNFPA, their staff works in over 150 countries to teach methods of family planning, reduce the spread of sexually transmitted diseases, support healthy pregnancies and childbirth, and to decrease violence against women.
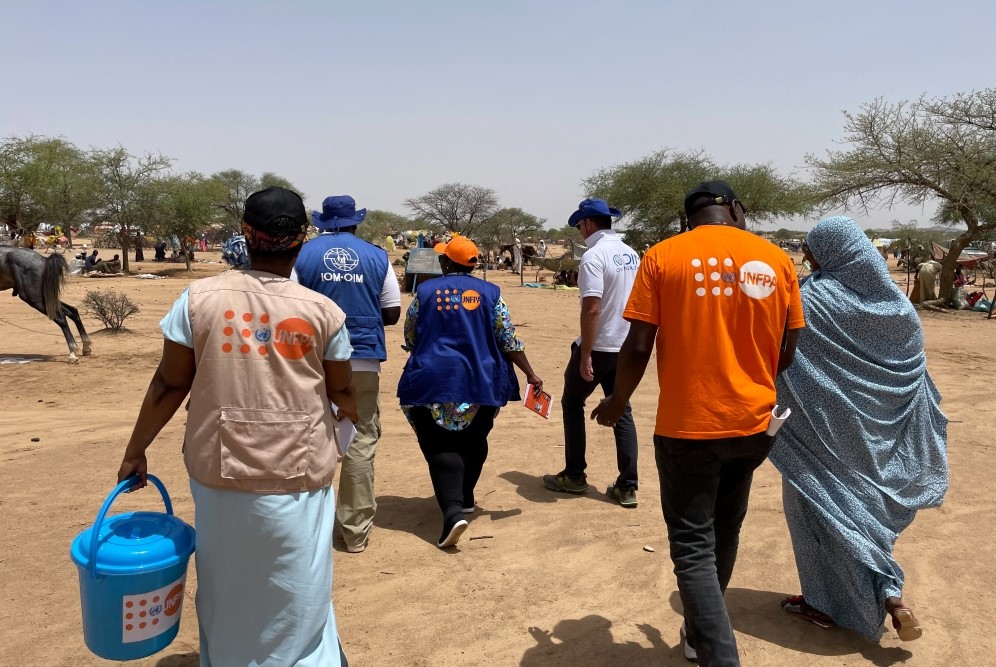

The UNFPA works alongside governments, foundations, charities, NGOs, other UN agencies, and private businesses to achieve its goals.
Although the UNFPA does work to distribute condoms and teach individuals methods on controlling the size of their families, the UNFPA does not provide financial or material resources for individuals to obtain an abortion or for forced sterilizations. Despite this, the United States has withdrawn its funding for UNFPA several times since the 1980s over a series of allegations that the UNFPA was funding coercive policies in totalitarian countries.
What Does the UNFPA Do?
Initially, the United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA) was set up primarily to collect data about childbirth and population growth, but as the world’s population began to grew rapidly in the 1960s, the agency began playing a more active role in providing funding, education, and resources needed to help countries, societies, and individuals take a more active role in family planning.
After three critical World Population Conferences in 1974 and 1984, the UNFPA broadened its role to include the advocacy of population control programs and laws, performing demographic projections, improving the legal status of women, and a broader focus on improving childhood and maternal health.
In 1994, the International Conference on Population and Development (ICPD) revolutionized the UNFPA’s mission, integrating population issues into the broader framework of development and a stronger call to action to combat global overpopulation and reduce infant and maternal mortality rates.
Who Owns the UNFPA?
The United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA) is an organization that is part of the United Nations and therefore is owned by all the 193 UN member states.
The UNFPA is led by an Executive Director (directly chosen by the UN Secretary-General) and an Executive Board consisting of representatives from 36 countries who serve on a rotating basis. The Executive Board simultaneously manages the UNFPA as well as two other UN agencies: the UNDP and UNOPS.
The UNFPA has had a total of five Executive Directors since its creation in 1969. The current UNFPA Executive Director is Dr. Natalia Kanem, who was appointed in 2017.

What does UNFPA Stand For?
The United Nations Population Fund was originally called the United Nations Fund for Population Activities (hence the acronym UNFPA) but was renamed in 1987. Despite this, the organization continues to use the acronym UNFPA.
The UNFPA’s overarching mission is to encourage sustainable economic and social development with a focus on reproductive and maternal health.
What Are the UNFPA’s Goals?
Today, the UNFPA’s goals, in alignment with the 2030 SDGs and the 1994 ICPD framework, are to assist:
- Eliminating unwanted pregnancies via family planning education and the use of contraceptives
- Safe pregnancies and child births
- The reduction of sexually transmitted disease
- The equality of women
- The end of gender-based violence
- Reducing maternal mortality
- Conducting censuses and research on population and development-related topics
Some of the biggest projects funded by the UNFPA include a campaign to eliminate obstetric fistula (which causes long-term injuries to women during childbirth), a campaign to end the practice of female genital mutilation (FGM), working to prevent the spread of HIV/AIDs, and a program to deliver reproductive health supplies during natural disasters and other emergencies.
Learn more about UNFPA open grants and tenders in the development sector, as well as opportunities for individual experts and professionals, on the organization’s profile page within the world’s largest development sector intelligence database DevelopmentAid.org.

